Star tracker is a high-precision device for measuring attitude, with the measurement reference being the star. It is the component with the highest attitude measurement accuracy in current satellite systems. It provides real-time information on the spatial position and reference feedback to the aircraft, and is widely used in spacecraft and satellites with relatively higher performance. The star sensors currently used in spacecraft have high stability and accuracy, as well as strong star tracking capabilities. At present, the measurement accuracy has reached sub angular seconds. Due to the relatively weak starlight, higher requirements are placed on the sensitivity of measurement equipment. The development of star sensor technology has gone through early star sensors, first generation non autonomous star sensors (CCD), second generation autonomous star sensors, and third generation star sensors (APS)。
In recent years, due to the rapid development of optical processing technology and detector technology, the performance of star sensors has been greatly improved, forming a particularly rich product system for star sensors.Normally, the working modes of star sensors include full sky recognition, self check mode, and star tracking mode. The above modes mainly include star tracking and all day recognition.For the full sky recognition mode, star sensors mainly recognize star maps within the full sky sphere to obtain the initial attitude.For star tracking mode, stars within the field of view can be tracked through star sensors. At the same time, based on the corresponding relationship between the successfully tracked navigation star image plane coordinates and the corresponding celestial coordinates, the three-axis attitude of the star sensor can be further calculated.Due to the requirement of the full sky region recognition mode that the matching search range of the star sensor is within the full sky sphere range, it will consume more time and also reduce the frequency of attitude updates. However, the star tracking mode only completes the navigation star search in local sky regions, which can greatly reduce the time consumption. If the star sensor is in normal operating mode, in most cases, the mode of the star sensor is in star tracking mode to ensure the frequency of updating data.
A star sensor is a high-precision attitude sensor with an accuracy of up to sub angular seconds. Figure 3 shows a typical structure diagram of a star sensor. This precise optoelectronic measurement device consists of image sensors, optical systems, external interfaces, signal processing circuits, and mechanical structures. Among them, the optical system consists of two parts: a lens and a light shield. When detecting stars, due to the influence of stray light, in severe cases, it may submerge the detected star target, causing a decrease in the performance of the star sensor and even making it unable to work. So, star sensors usually install light shields, mainly to further suppress or eliminate stray light entering the image sensor, and to further expand the working range of star sensors throughout the entire sky. The lens section will image stars at infinity on the image sensor. The signal processing circuit is mainly used for sensor driving and controlling timing. It can also perform functions such as identifying star maps and extracting star points, ultimately completing the output of three-axis attitude information.
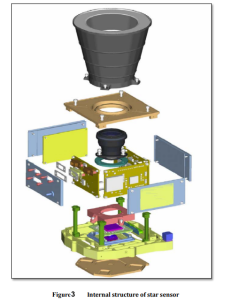
So far, star tracker are still the most accurate sensors for attitude measurement on spacecraft (capable of reaching angular second or even sub angular second levels), playing an irreplaceable role in high-precision surveying, remote sensing, and formation flying. Interpreting the composition of star trackers from the perspective of their working modes can help us better understand the magnificent scenery of the aerospace manufacturing industry.
Send us a message,we will answer your email shortly!