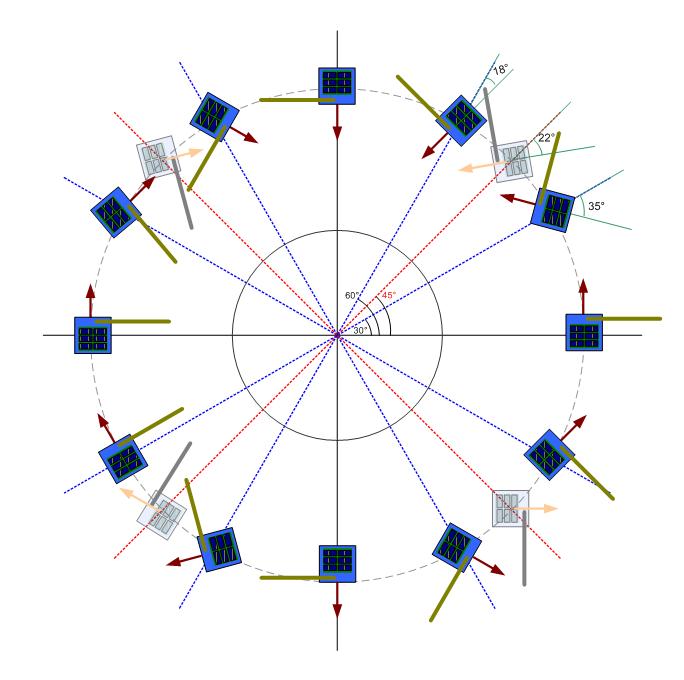
Satellite attitude control is the process of maintaining the correct orientation of a spacecraft. In simpler terms, it ensures that the satellite remains aligned to perform its tasks efficiently, such as communication, data collection, and navigation. The attitude control system (ACS) uses various components like reaction wheels, magnetorquers, and control moment gyroscopes to adjust the satellite’s position.
Maintaining accurate orientation is vital for ensuring that satellites perform their missions effectively. The following areas benefit from precise attitude control:
Communication: Keeps antennas correctly pointed at Earth or other satellites.
Imaging: Ensures sensors stay aligned to capture clear images.
Navigation: Helps satellites maintain their correct trajectory during flight.
The Satellite Attitude Control Module is a vital system for managing a satellite’s orientation. It integrates several key components:
Reaction wheels play a crucial role in providing fine attitude control. By adjusting the wheel speed, the satellite’s orientation is changed with great precision. These wheels are especially useful for accurately controlling attitude without relying on external forces.
Magnetorquers use Earth’s magnetic field to adjust the satellite’s orientation. These are effective in low Earth orbit (LEO) and provide a low-power solution for attitude adjustments, complementing reaction wheels.
Sun sensors help determine the satellite’s orientation by detecting the position of the Sun. Star trackers, on the other hand, provide high-precision attitude determination by comparing star fields to known star catalogs.
For larger satellites, CMGs are used for more advanced and precise attitude control. These gyroscopes provide superior stability and are particularly effective in large spacecraft that require large movements.
To maintain orientation, satellites rely on a combination of sensors and actuators. For instance, when an attitude change is needed, the control module processes data from sun sensors, star trackers, and other instruments. The module then commands the reaction wheels or magnetorquers to make the necessary adjustments.
Attitude control requires continuous real-time monitoring. Whenever an adjustment is necessary, the ACM makes small corrections to ensure that the satellite remains properly aligned. This feedback loop allows satellites to adapt to changing conditions in orbit.
Satellite attitude control is used in many types of satellites:
For communication satellites, accurate attitude control ensures uninterrupted signal transmission. For example, antennas need to stay correctly pointed toward Earth to maintain contact.
Earth observation satellites rely on precise attitude control to capture clear, accurate images. A stable orientation ensures that the satellite stays aligned with its target area, crucial for precise data collection.
Satellites and spacecraft used in space exploration require the ability to adjust their orientation for navigation and data collection. Accurate attitude control is essential for these missions, which often involve long distances and changing environments.
Satellite attitude control is critical for the success of space missions. By maintaining accurate orientation, the Satellite Attitude Control Module ensures that communication, navigation, and data collection processes function smoothly. The ACM integrates a variety of systems to achieve this precision, making it a fundamental component of modern satellite design.
For more information about satellite attitude control systems and how they can improve your satellite mission’s performance, click here to learn more.
Send us a message,we will answer your email shortly!