Satellite sensors are devices that collect data about the satellite’s environment and its internal systems. These sensors allow satellites to monitor conditions such as temperature, orientation, radiation, and even detect movement or changes in position. The data is transmitted back to Earth for analysis and use in various applications, such as weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, and communication.
There are several types of satellite sensors, each designed for specific purposes. Below are some of the most commonly used sensors in satellite technology:
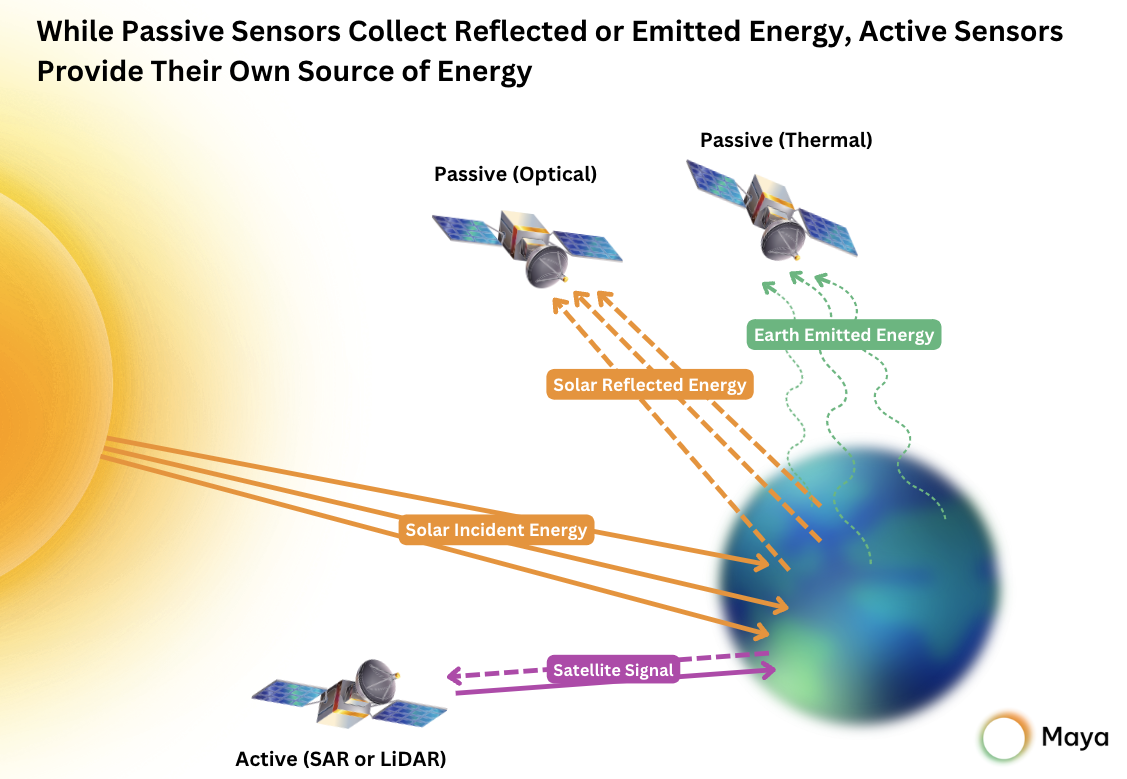
Imaging sensors capture visual data, including photographs and videos, which are vital for Earth observation, surveillance, and scientific research. These sensors use optical and infrared technologies to gather information in different light spectra.
These sensors monitor the temperature of the satellite’s components and surrounding space. They ensure that the satellite stays within safe operational limits and can help prevent overheating or malfunction.
Radiation sensors measure the levels of ionizing radiation in space. These sensors help protect the satellite’s electronics and systems from harmful radiation that could affect performance or cause damage.
Magnetic field sensors detect changes in the satellite’s surroundings, helping with orientation control and navigation. They are essential for ensuring the satellite’s stability and alignment in space.
Sun sensors track the position of the sun to aid in orientation control. By providing data on the satellite’s alignment relative to the sun, they help in positioning solar panels to optimize power generation.
Satellite sensors are integral to space missions, enabling satellites to perform their tasks effectively. For instance:
Environmental Monitoring: Sensors on Earth observation satellites measure atmospheric and surface conditions, which are used for weather forecasting, climate studies, and natural disaster management.
Navigation and Positioning: Sensors help navigation satellites maintain their orientation and positioning, ensuring they can provide accurate geolocation data to ground systems.
Scientific Research: Scientific missions rely on sensors to gather data from space, such as measuring cosmic radiation or analyzing distant celestial bodies.
Satellite sensors are crucial for gathering real-time data and maintaining satellite functionality in the harsh environment of space. They ensure that satellites operate efficiently and safely, enabling a variety of applications such as communications, scientific research, and defense.
Accuracy: Satellite sensors provide accurate, high-quality data that is essential for mission success.
Efficiency: By monitoring internal systems and external conditions, sensors help optimize satellite performance, reducing the likelihood of malfunctions.
Cost-Effective: Sensors allow for the early detection of issues, preventing expensive repairs or satellite failures.
Satellite sensors find applications in various fields:
Weather Forecasting: Sensors on weather satellites gather data on cloud patterns, temperature, and humidity to help predict weather conditions.
Communication: Communication satellites use sensors to maintain proper alignment for signal transmission.
Defense and Security: Satellites equipped with imaging sensors and radiation detectors help monitor national security and defense activities.
Choosing the right satellite sensors depends on the specific mission and operational needs. For Earth observation, high-resolution imaging sensors might be required, while temperature and radiation sensors are more critical for satellite health monitoring. Understanding the mission’s objectives is key to selecting the best sensors.
Send us a message,we will answer your email shortly!